Hydrogen and Ammonia: Alternative Energy Commodities That Will Shape the Next Decade
Hydrogen and Ammonia: Alternative Energy Commodities That Will Shape the Next Decade
As the world accelerates toward a low-carbon future, hydrogen and ammonia have emerged as promising energy commodities that can play a pivotal role in the future of clean energy. According to current estimates, the global hydrogen market is expected to reach approximately $500 billion by 2030, driven by growing commitments from governments and companies toward achieving carbon neutrality goals.
“Hydrogen is not just an alternative energy carrier, but the cornerstone in building a sustainable, carbon-free global economy. And ammonia is the key to transporting this energy on a global scale.”

Types of Hydrogen: Colors of Future Energy
Green Hydrogen
Produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power, making it completely free from carbon emissions. It’s considered the optimal solution for the future, despite its current high cost.
Expected Cost in 2030: $1.5-2/kg
Blue Hydrogen
Produced from fossil fuels, but with carbon capture and storage. It is considered an important transitional solution towards a green hydrogen economy, offering lower cost with significant emissions reduction.
Emissions Reduction: Up to 90% compared to gray hydrogen
Gray Hydrogen
Currently produced from natural gas or coal without carbon capture, representing about 95% of global production. Primarily used in ammonia production and refining.
Share of Global Market: 95%
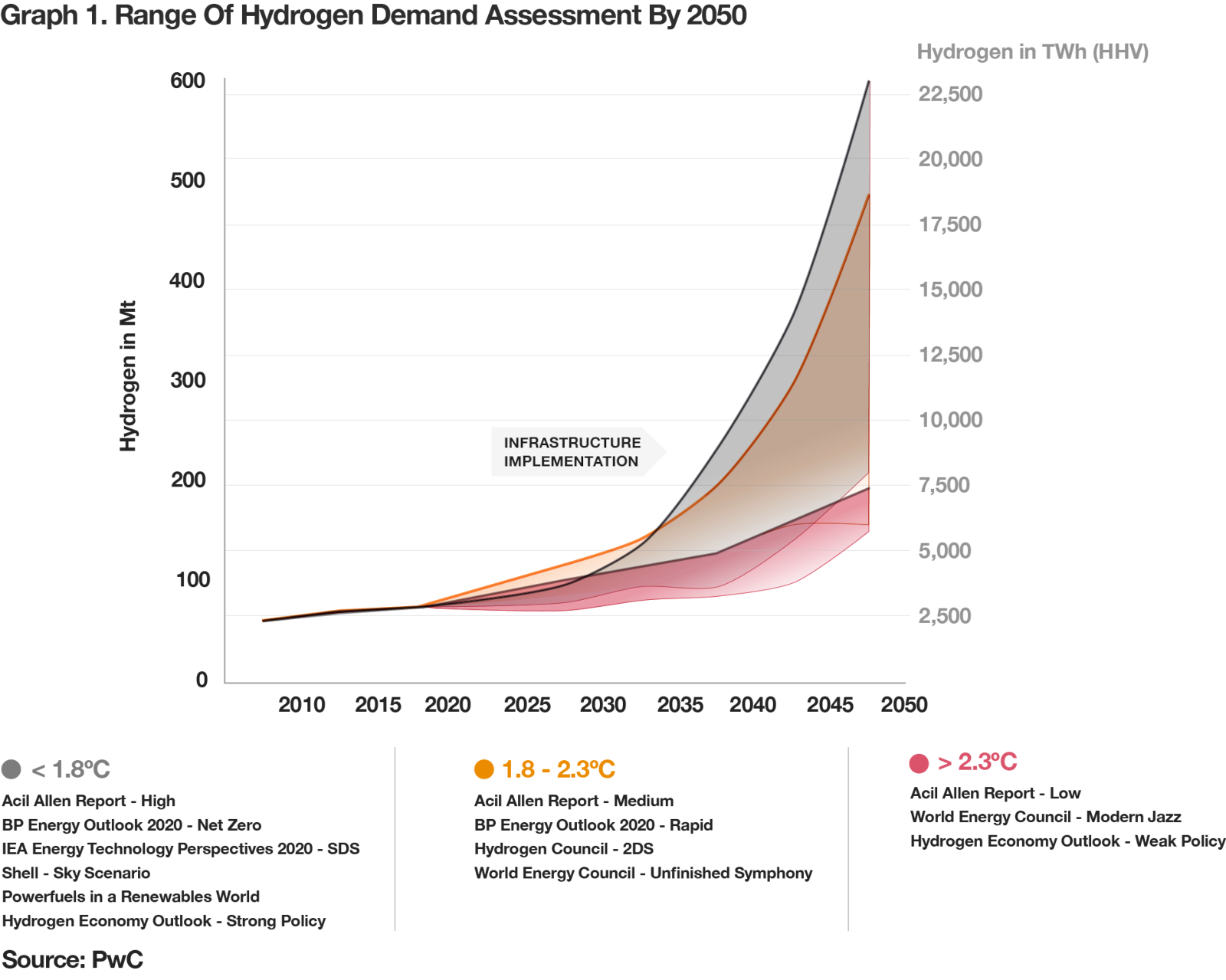
Projected reduction in green hydrogen production costs through 2030
Ammonia: The Strategic Hydrogen Carrier
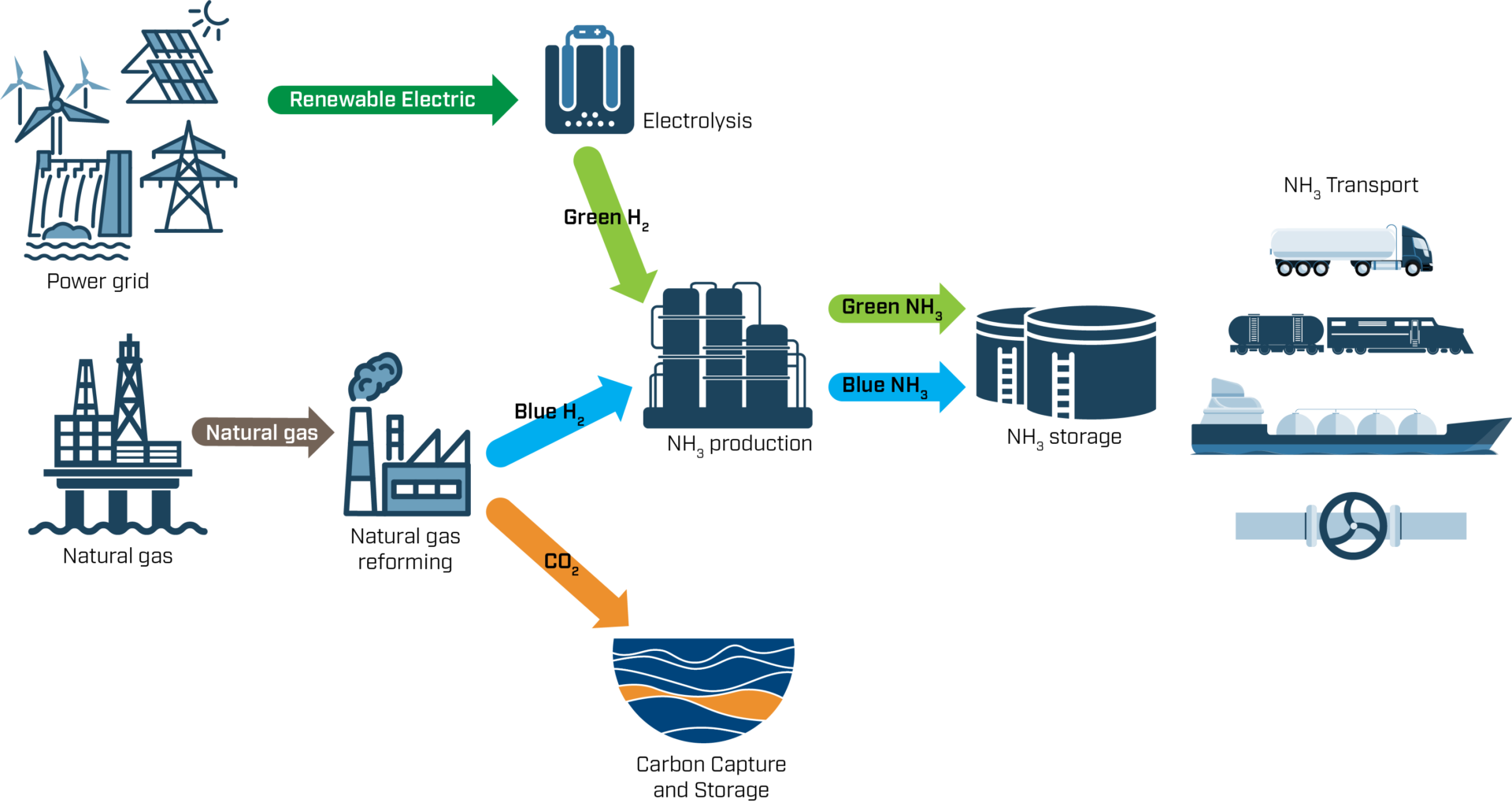
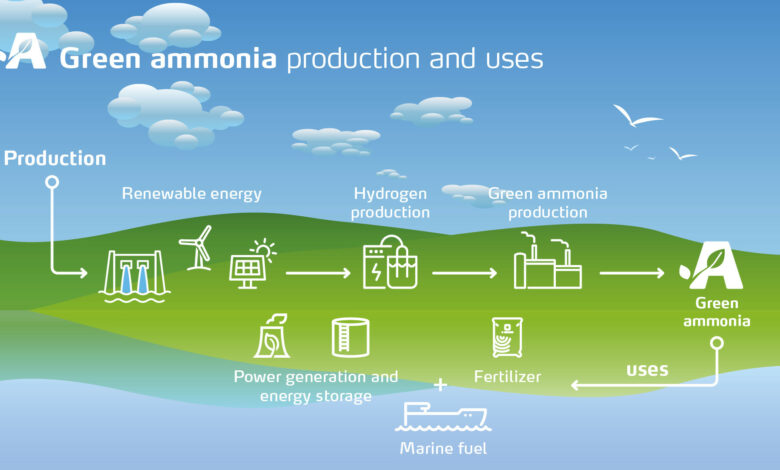
Ammonia value chain: from production to transportation and use
Ammonia (NH₃) is considered an ideal solution for transporting hydrogen over long distances. Although hydrogen carries high energy density relative to its weight, its large volume and difficulties in storage and transport pose significant logistical challenges.
Why Ammonia?
- Can be liquefied more easily than hydrogen (at -33°C compared to -253°C for hydrogen)
- Contains 17.6% hydrogen by weight
- Existing global infrastructure for transport and storage
- Can be used directly as fuel or converted back to hydrogen
According to estimates, the green ammonia market is expected to reach $11 billion by 2030, with a special focus on its use in maritime transport and energy-intensive industries.
Hydrogen Market: Growth and Investment Forecasts
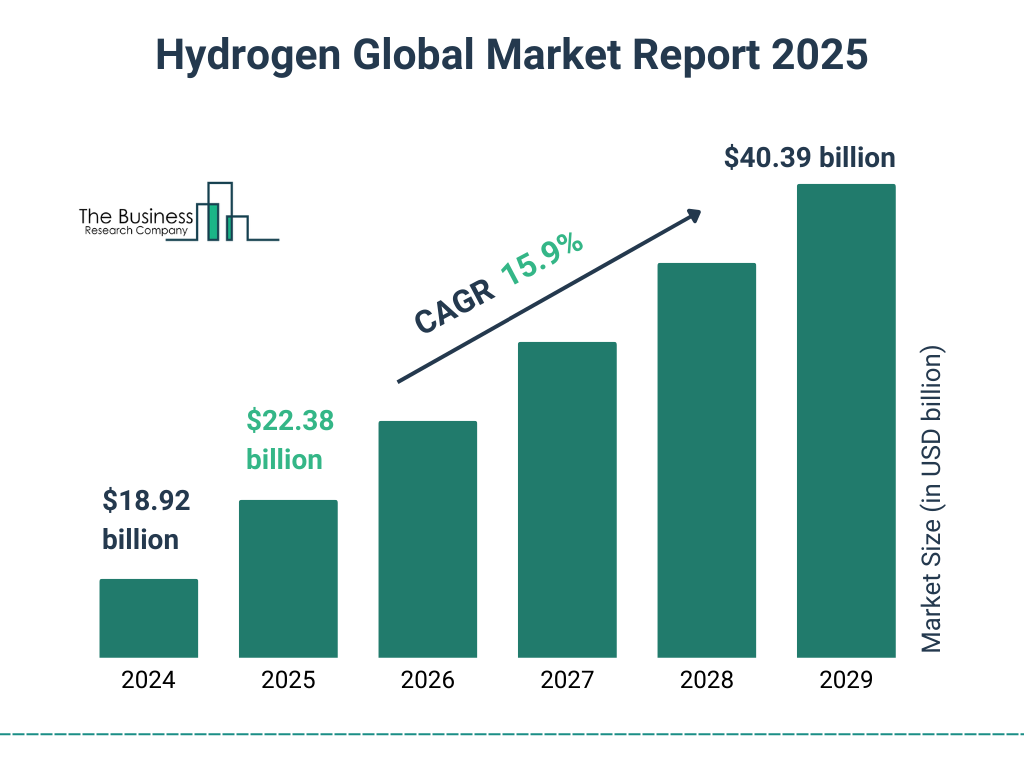
Global hydrogen market growth forecasts through 2032
Global Investments
Hydrogen and ammonia investments are experiencing unprecedented growth, with announced projects valued at more than $300 billion through 2030. Europe, the Middle East, and Australia lead the list of regions attracting the largest investments.
- European Union: Allocated €470 billion for green hydrogen development through 2050
- Saudi Arabia: NEOM green hydrogen project valued at $5 billion
- Australia: Green hydrogen and ammonia projects worth $30 billion
Key Growth Drivers
- Supportive government policies and financial backing for green projects
- Global corporate commitments to carbon neutrality
- Declining costs of renewable energy production
- Evolution of electrolysis technologies and increasing efficiency
- Enhanced international cooperation in technology transfer and project development
Leading Companies and Promising Investment Opportunities
Production Technology Companies
- Nel ASA Electrolysis
- ITM Power PEM Systems
- McPhy Energy Storage & Production
- Enapter AEM Systems
Traditional Energy Companies
- Air Liquide Blue Hydrogen
- Linde Infrastructure
- Shell Integrated Projects
- Total Energies Green Hydrogen
Ammonia Companies
- CF Industries Green Ammonia
- Yara International Production & Distribution
- OCI Global Blue Ammonia
- Fertiglobe Middle East Projects
Investment Strategies
Long-term Investments
- Investing in leading production technology companies
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) specialized in hydrogen and clean energy
- Infrastructure companies developing hydrogen transport and distribution networks
- Traditional energy companies transitioning toward a hydrogen economy
Risk Management
- Diversifying investments across different stages of the value chain
- Evaluating regulatory and technological risks for each company
- Monitoring developments in government policies and financial support
- Balancing between startups and established companies in the portfolio
Industrial Applications and Key Uses

Various hydrogen applications in industrial sectors
Energy-Intensive Industries
Industries such as steel, cement, and petrochemicals represent a significant opportunity for green hydrogen use, as these sectors contribute about 20% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Steel production using hydrogen instead of coal
- High-temperature heat in cement manufacturing
- Green ammonia production for fertilizers
Transportation Sector
The transportation sector represents one of the most important future areas for hydrogen use, especially in heavy transport and long distances where electric batteries face challenges.
- Fuel cell cars and trucks
- Hydrogen-powered trains (such as Alstom projects in Europe)
- Maritime transport using ammonia as fuel
- Low-carbon aviation using liquified hydrogen
Challenges and Future Prospects
Current Challenges
- High cost of green hydrogen production
- Need for large-scale infrastructure
- Energy conversion efficiency in the value chain
- Competition with other alternative energy sources
- Technical challenges in storage and transport
Emerging Trends
- Development of more efficient electrolysis systems
- Creation of hydrogen valleys in different regions
- Enhanced international cooperation in hydrogen transport
- Integration of hydrogen production with renewable energy sources
- Ammonia cracking technologies for efficient hydrogen extraction
2030-2050 Outlook
- Green hydrogen reaching cost parity with gray by 2030
- 10% share of global energy demand by 2050
- Reduction of 80 billion tons of CO₂ emissions by 2050
- About 30 million jobs related to the hydrogen economy
- Global hydrogen economy worth $2 trillion
“We are on the threshold of a radical transformation in the global energy sector, and hydrogen and ammonia will be at the heart of this transformation. Investors who enter this field now are positioning themselves strategically to benefit from the tremendous growth expected over the coming decades.”
Conclusion
Hydrogen and ammonia as future energy commodities represent promising investment opportunities in the global transition to a low-carbon economy. With continuing decreases in production costs, technological advancements, and supportive policies, this sector is expected to experience exceptional growth over the next decade.
Investment opportunities are diverse across the entire value chain, from production technology companies to infrastructure projects and industrial application companies. Strategic investors will look for balanced opportunities that combine promising startups and established companies transitioning toward a hydrogen economy.
Despite existing challenges, strong governmental and institutional commitments to climate goals, along with positive technological trends, make hydrogen and ammonia key players in the future of energy. For investors able to tolerate short-term fluctuations, this sector can represent an exceptional opportunity to achieve long-term returns while contributing to building a more sustainable future.