Why Murphy’s Classic is the Most Important
Discover how John J. Murphy's masterpiece revolutionized technical analysis education and became the definitive guide that transformed millions of traders' understanding of financial markets worldwide


Why “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” is Considered the Best?
The Legendary Book: Why Murphy’s Classic is the Most Important
The Book That Changed Technical Analysis Understanding for Millions
The Revolutionary Impact of Murphy’s Masterpiece
In the vast ocean of financial literature, few books have achieved the legendary status of “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” by John J. Murphy. This masterpiece hasn’t just educated traders; it has fundamentally transformed how millions approach market analysis and trading decisions across the globe.
Since its first publication in 1986, this book has stood as the undisputed “Bible” of technical analysis, earning its place on the desks of professional traders, institutional analysts, and retail investors alike. But what makes this particular book so special that even after nearly four decades, it remains the gold standard for technical analysis education?

“The fundamentalist studies the cause of market movement, while the technician studies the effect. The effect is all that we need to know.”
— John J. Murphy
This profound statement encapsulates the very essence of Murphy’s revolutionary approach to market analysis. While others were debating economic theories and fundamental factors, Murphy provided a clear, practical framework that focused on what truly matters: price action and market behavior.
John J. Murphy: The Legend Behind the Bible
The Man Who Revolutionized Trading Education
With over four decades of experience in the field, John J. Murphy stands as one of the most respected figures in technical analysis. His journey began in the 1970s when he started working as a technical analyst, eventually becoming a renowned market commentator and educator whose influence extends far beyond traditional trading circles.
Murphy’s expertise isn’t limited to stocks alone. His comprehensive understanding encompasses futures markets, commodities, currencies, and bonds, making his approach truly universal. This broad perspective is precisely what sets his work apart from other technical analysis books that focus on single asset classes.
40+ Years
Market Analysis Experience
Multiple Markets
Stocks, Futures, Commodities
Global Impact
Millions of Traders Educated
The Foundation of Modern Technical Analysis
Murphy’s contribution to the field extends beyond just writing books. He has been instrumental in developing and popularizing many of the technical analysis concepts that traders use today. His work on intermarket analysis, chart patterns, and indicator interpretation has become the foundation upon which modern technical analysis is built.
What makes Murphy’s approach unique is his ability to distill complex market concepts into understandable, actionable insights. His writing style is clear and concise, avoiding unnecessary jargon while providing practical guidance that can be immediately applied in real-world trading scenarios.
The Historical Evolution: From 1986 to Modern Era
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Introductio_to_Technical_Analysis_Price_Patterns_Sep_2020-02-59df8834491946bcb9588197942fabb6.jpg)
The Original Vision: 1986 Foundation
When Murphy first published “Technical Analysis of the Futures Markets” in 1986, the financial world was vastly different. Personal computers were just beginning to enter trading floors, and most analysis was still done by hand on paper charts. Yet Murphy’s vision was forward-thinking, establishing principles that would remain relevant through decades of technological revolution.
The Evolution to Financial Markets
The transformation from “Technical Analysis of the Futures Markets” to “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” wasn’t just a title change—it represented a fundamental expansion of scope. Murphy recognized that the principles of technical analysis were universal, applicable across all financial instruments and markets.
Original Edition Features (1986)
- Futures market focus
- Basic chart patterns
- Traditional indicators
- Manual charting methods
Modern Edition Enhancements
- All financial markets
- Candlestick charting
- Intermarket analysis
- Computer-based tools
Adaptation to Technological Revolution
The impact of Murphy’s work extends far beyond individual trading success stories. It has shaped entire educational curricula in business schools, influenced the development of trading software, and established the foundational principles that continue to guide technical analysis education worldwide. This adaptability to changing times while maintaining core principles is what makes the book truly timeless.
Why It’s Called “The Bible” of Technical Analysis
The term “Bible” isn’t used lightly in financial circles, yet Murphy’s book has earned this distinction through decades of proven value and universal acceptance. But what exactly qualifies a book to be considered the definitive authority in its field?
Comprehensive Coverage
Unlike books that focus on specific aspects of technical analysis, Murphy’s masterpiece covers every essential topic a trader needs to know. From basic chart construction to advanced pattern recognition, from simple moving averages to complex oscillators, the book leaves no stone unturned.
This comprehensive approach means that both beginners and experienced professionals can find value within its pages, making it a reference that traders return to throughout their careers.
Universal Acceptance
Professional trading institutions worldwide use Murphy’s book as their standard training material. From Wall Street trading floors to international investment banks, the principles outlined in this book form the foundation of technical analysis education.
This universal acceptance isn’t accidental—it’s the result of proven effectiveness across different markets, time frames, and trading styles.
Key Factors That Earned the “Bible” Status
Global Recognition
Translated into dozens of languages, used worldwide
Timeless Principles
Relevant across decades of market evolution
Community Standard
Referenced by professionals and educators globally
The Ultimate Reference Guide
What truly sets Murphy’s book apart is its role as the ultimate reference guide. Traders don’t just read it once and put it away—they return to it repeatedly throughout their careers. Whether they’re encountering a new chart pattern, trying to understand a complex indicator, or seeking to refresh their knowledge of fundamental principles, Murphy’s book provides the answers they need.
Core Content: The Foundation of Technical Analysis
The strength of Murphy’s book lies not just in its breadth, but in how it builds knowledge systematically. Each chapter builds upon the previous one, creating a comprehensive framework that transforms novice traders into knowledgeable analysts.
Philosophical Foundations
Murphy begins with the philosophical underpinnings of technical analysis, explaining the three fundamental assumptions that form the basis of all technical analysis: market action discounts everything, prices move in trends, and history repeats itself.
This philosophical grounding isn’t just academic—it provides traders with the confidence to trust their technical analysis even when fundamental news seems to contradict market action.
Chart Construction and Types
From basic line charts to complex candlestick patterns, Murphy covers every type of chart construction method. He explains not just how to create these charts, but more importantly, when and why to use each type.
This practical approach ensures that readers understand the tool selection process, enabling them to choose the most appropriate charting method for their specific analysis needs.

Trend Analysis
Support, resistance, trendlines, and channels
Pattern Recognition
Head and shoulders, triangles, flags, and more
Volume Analysis
Price-volume relationships and confirmation signals
The Systematic Approach
What makes Murphy’s content particularly valuable is its systematic approach to market analysis. Rather than presenting isolated techniques, he shows how different analytical tools work together to create a comprehensive market assessment. This integrated approach is what separates professional analysis from amateur guesswork.
Key Innovations That Changed Everything
Murphy’s book wasn’t just a compilation of existing knowledge—it introduced several groundbreaking concepts that revolutionized how traders approach market analysis. These innovations continue to influence trading methodology decades after their introduction.
Intermarket Analysis Revolution
One of Murphy’s most significant contributions was popularizing intermarket analysis—the study of relationships between different asset classes. He demonstrated how bonds, stocks, commodities, and currencies influence each other, providing traders with a macro view of market dynamics.
This concept was revolutionary because it moved technical analysis beyond single-market focus, showing traders how to use cross-market relationships for better timing and confirmation of their analysis.

Murphy’s Innovation Framework
Before Murphy:
- • Single-market focus
- • Limited pattern recognition
- • Basic indicator usage
- • Isolated analysis approach
Murphy’s Contribution:
- • Intermarket relationships
- • Comprehensive pattern catalog
- • Integrated indicator systems
- • Holistic market perspective
Candlestick Integration
While candlestick charting originated in Japan centuries ago, Murphy was instrumental in integrating these techniques with Western technical analysis. He showed how candlestick patterns could enhance traditional chart pattern analysis, providing additional confirmation signals and earlier entry/exit points.
Computer-Age Adaptation
Perhaps most importantly, Murphy successfully bridged the gap between traditional manual charting and computer-based analysis. He showed how classic principles could be applied using modern technology, ensuring that technical analysis remained relevant in the digital age.
Chart Patterns and Advanced Techniques
Murphy’s treatment of chart patterns goes far beyond simple pattern recognition. He provides the psychological reasoning behind each pattern, explains the market dynamics that create them, and most importantly, teaches traders how to trade them profitably.
Classic Pattern Mastery
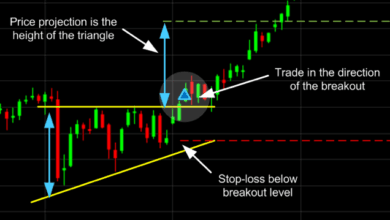
The book covers all major chart patterns with unprecedented detail. From reversal patterns like head and shoulders to continuation patterns like flags and pennants, Murphy explains not just what to look for, but how to measure price targets and manage risk.
Advanced Applications
Beyond basic patterns, Murphy delves into advanced applications that separate professional traders from amateurs. He covers complex formations, pattern failures, and how to use patterns in different time frames for maximum effectiveness.
Professional Techniques
- • Multiple time frame pattern confirmation
- • Volume-based pattern validation
- • Pattern failure trading strategies
- • Risk management within patterns

Technical Indicators Mastery
Murphy’s coverage of technical indicators is comprehensive yet practical. He doesn’t just explain how indicators work—he shows when to use them, how to combine them effectively, and most crucially, how to avoid the common pitfalls that trap inexperienced traders.
Trend Indicators
Moving averages, MACD, trend lines
Momentum Oscillators
RSI, Stochastics, Williams %R
Volume Indicators
OBV, A/D line, volume patterns
Integrated Analysis Methodology
Perhaps Murphy’s greatest contribution is teaching traders how to integrate multiple analytical techniques into a cohesive methodology. Rather than relying on single indicators or isolated patterns, he demonstrates how professional analysts combine various tools for higher probability trades.
The Multi-Layered Approach
Murphy’s methodology involves multiple layers of analysis, each providing confirmation or warning signals. This approach significantly reduces false signals while increasing the reliability of trading decisions.
Layer 1: Trend Analysis
- Primary trend identification
- Support and resistance levels
- Trend line analysis
Layer 2: Pattern Recognition
- Chart pattern identification
- Candlestick formations
- Pattern completion signals
Murphy’s Integration Principle
“The best trading opportunities occur when multiple analytical techniques point in the same direction.”
This principle forms the foundation of professional market analysis
Time Frame Analysis
Murphy introduced the concept of multiple time frame analysis, showing traders how to use different chart time frames to gain a complete market perspective. This technique helps traders avoid the tunnel vision that comes from focusing on a single time frame.
Long-term View
Monthly/Weekly charts for major trend
Intermediate Analysis
Daily charts for pattern recognition
Timing Entry
Intraday charts for precise execution
Impact on Financial Education Worldwide
The influence of Murphy’s work extends far beyond individual trading success stories. It has shaped entire educational curricula in business schools, influenced the development of trading software, and established the foundational principles that continue to guide technical analysis education worldwide.
Academic Integration
Business schools and finance programs worldwide have integrated Murphy’s methodologies into their curricula. The book serves as the primary textbook for technical analysis courses, ensuring that new generations of financial professionals are grounded in proven analytical techniques.
This academic adoption has legitimized technical analysis as a serious discipline, moving it from the realm of speculation to recognized analytical methodology.
Professional Certification
The Chartered Market Technician (CMT) program, the premier professional certification for technical analysts, uses Murphy’s book as core required reading. This endorsement by the industry’s leading certification body underscores the book’s authoritative status.
Thousands of professionals have earned their CMT designation with Murphy’s book as their foundation, creating a global community of analysts trained in his methodologies.
Global Educational Impact
Technology Integration
Murphy’s principles have been integrated into virtually every major trading platform and charting software. From MetaTrader to TradingView, from Bloomberg terminals to proprietary bank systems, the indicators, patterns, and methodologies described in Murphy’s book form the backbone of modern trading technology.
This technological integration ensures that Murphy’s teachings reach millions of traders worldwide, democratizing access to professional-grade analytical tools and maintaining the relevance of his work in the digital age.
Comparative Analysis with Other Trading Books
While many excellent trading books exist, Murphy’s work stands apart in several key areas. Understanding these distinctions helps explain why it has maintained its position as the definitive technical analysis reference for decades.
Scope and Comprehensiveness
Murphy’s Approach
- Covers all major markets and instruments
- Integrates multiple analytical methods
- Suitable for all experience levels
- Timeless principles with modern applications
Other Books Typically
- Focus on specific markets or strategies
- Emphasize single analytical approaches
- Target specific experience levels
- May become outdated with market changes
What Sets Murphy Apart
“While other books teach you what to think, Murphy’s book teaches you how to think about markets. This fundamental difference creates analysts rather than mere pattern followers.”
— Professional Trading Community Consensus
Educational Value Comparison
Murphy’s Book
- • Systematic learning progression
- • Theory backed by practical examples
- • Comprehensive reference value
- • Universal market application
- • Time-tested methodologies
Strategy-Focused Books
- • Specific trading systems
- • Limited market scope
- • Narrow application range
- • May lack theoretical foundation
- • Often market-condition dependent
Academic Texts
- • Heavy theoretical focus
- • Limited practical application
- • Complex mathematical models
- • Often outdated examples
- • Difficult for beginners
Longevity and Relevance
The true test of any educational resource is its ability to remain relevant over time. Murphy’s book has not only maintained its relevance but has actually grown in importance as markets have evolved. This longevity is a testament to the fundamental nature of the principles it teaches— principles that transcend specific market conditions or technological changes.
Practical Application and Real-World Implementation
The ultimate measure of any trading book is how well its concepts translate into real-world trading success. Murphy’s book excels in this area, providing clear guidance on how to implement theoretical concepts in actual trading situations.
From Theory to Practice
Step-by-Step Implementation
Murphy doesn’t just explain what chart patterns look like—he provides detailed instructions on how to identify them in real-time, how to measure price targets, and how to manage risk throughout the trade.
Real Market Examples
The book is filled with actual market examples that demonstrate how the concepts work in practice. These aren’t idealized textbook cases—they’re real market situations that show both successful applications and common pitfalls to avoid.
Example Categories
- • Stock market pattern breakouts
- • Commodity trend reversals
- • Currency pair correlations
- • Bond market indicator signals
Building a Trading System
One of the book’s greatest strengths is showing readers how to combine individual techniques into a complete trading system. Murphy provides frameworks for building systematic approaches that can be consistently applied across different markets and conditions.
Analysis Phase
Market scanning and opportunity identification
Execution Phase
Entry timing and position management
Risk Management
Stop losses and portfolio protection
Success Story Framework
“Murphy’s book provided me with a complete framework for market analysis. Within six months of studying and applying his methods, my trading consistency improved dramatically. The key was learning to combine multiple confirming signals rather than relying on single indicators.”
— Professional Portfolio Manager
Adaptation to Modern Markets
While markets have evolved significantly since the book’s first publication, the core principles remain remarkably applicable. Murphy’s emphasis on price action, volume analysis, and market psychology continues to provide valuable insights in today’s algorithm-driven markets. The book’s enduring practical value is a fascinating tale of adaptation, innovation, and enduring relevance in an ever-changing financial landscape.
Conclusion and Recommendations
After nearly four decades in print, “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” by John J. Murphy continues to earn its reputation as the definitive guide to market analysis. Its enduring success isn’t accidental—it’s the result of comprehensive coverage, practical applicability, and timeless principles that transcend market conditions and technological changes.
Why This Book Remains Essential Today
For Beginners
New traders will find a systematic introduction to market analysis that builds knowledge progressively. The book’s clear explanations and practical examples provide a solid foundation that prevents the common mistakes that plague novice traders.
- Comprehensive introduction to all major concepts
- Step-by-step learning progression
- Practical application guidance
For Experienced Traders
Even seasoned professionals benefit from Murphy’s integrated approach and advanced concepts. The book serves as an excellent reference for refreshing knowledge and discovering new applications of familiar techniques.
- Advanced integration techniques
- Comprehensive reference value
- Professional methodology refinement
Final Assessment
Our Recommendation
Whether you’re just starting your trading journey or you’re a seasoned professional looking to refine your analytical skills, “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” deserves a place in your library. It’s not just a book you read once—it’s a reference you’ll return to throughout your trading career.
The investment in this book—both in terms of money and time—will pay dividends for years to come. In a field where knowledge truly is power, Murphy’s book provides the foundation upon which trading success is built.
Don’t just take our word for it—join the millions of traders worldwide who have discovered why this book truly deserves its reputation as “The Bible” of technical analysis.